List of moments of inertia
Moment of inertia, denoted by I, measures the extent to which an object resists rotational acceleration about a particular axis; it is the rotational analogue to mass (which determines an object's resistance to linear acceleration). The moments of inertia of a mass have units of dimension ML2 ([mass] × [length]2). It should not be confused with the second moment of area, which has units of dimension L4 ([length]4) and is used in beam calculations. The mass moment of inertia is often also known as the rotational inertia, and sometimes as the angular mass.
For simple objects with geometric symmetry, one can often determine the moment of inertia in an exact closed-form expression. Typically this occurs when the mass density is constant, but in some cases the density can vary throughout the object as well. In general, it may not be straightforward to symbolically express the moment of inertia of shapes with more complicated mass distributions and lacking symmetry. When calculating moments of inertia, it is useful to remember that it is an additive function and exploit the parallel axis and perpendicular axis theorems.
This article mainly considers symmetric mass distributions, with constant density throughout the object, and the axis of rotation is taken to be through the center of mass unless otherwise specified.
Moments of inertia
[edit]Following are scalar moments of inertia. In general, the moment of inertia is a tensor, see below.
| Description | Figure | Moment(s) of inertia | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Point mass M at a distance r from the axis of rotation. | 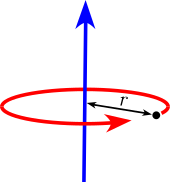
|
A point mass does not have a moment of inertia around its own axis, but using the parallel axis theorem a moment of inertia around a distant axis of rotation is achieved. | |
| Two point masses, m1 and m2, with reduced mass μ and separated by a distance x, about an axis passing through the center of mass of the system and perpendicular to the line joining the two particles. | 
|
Both bodies are treated as point masses: dots of different size indicate the difference in masses of bodies, not in their sizes. | |
| Thin rod of length L and mass m, perpendicular to the axis of rotation, rotating about its center. | 
|
[1] | This expression assumes that the rod is an infinitely thin (but rigid) wire. This is a special case of the thin rectangular plate with axis of rotation at the center of the plate, with w = L and h = 0. |
| Thin rod of length L and mass m, perpendicular to the axis of rotation, rotating about one end. | 
|
[1] | This expression assumes that the rod is an infinitely thin (but rigid) wire. This is also a special case of the thin rectangular plate with axis of rotation at the end of the plate, with h = L and w = 0. |
| Thin circular loop of radius r and mass m.. | 
|
This is a special case of a torus for a = 0 (see below), as well as of a thick-walled cylindrical tube with open ends, with r1 = r2 and h = 0 | |
| Thin, solid disk of radius r and mass m. | 
|
This is a special case of the solid cylinder, with h = 0. That is a consequence of the perpendicular axis theorem. | |
| A uniform annulus (disk with a concentric hole) of mass m, inner radius r1 and outer radius r2 | 
|
|
|
| An annulus with a constant area density |
|
||
| Thin cylindrical shell with open ends, of radius r and mass m. | 
|
[1] | The expression ″thin″ indicates that the shell thickness is negligible. It is a special case of the thick-walled cylindrical tube of the same mass for r1 = r2.
Also, a point mass m at the end of a rod of length r has this same moment of inertia and the value r is called the radius of gyration. |
| Solid cylinder of radius r, height h and mass m. | 
|
[1] |
This is a special case of the thick-walled cylindrical tube, with r1 = 0. |
| Thick-walled cylindrical tube with open ends, of inner radius r1, outer radius r2, length h and mass m. | 
|
[1]
[2]
|
The given formula is for the plane passing through the center of mass,
which coincides with the geometric center of the cylinder.
If the xy plane is at the base of the cylinder, i.e. offset by then by the parallel axis theorem the following formula applies: |
| With a density of ρ and the same geometry |
|
||
| Regular tetrahedron of side s and mass m with an axis of rotation passing through a tetrahedron's vertex and its center of mass | 
|
||
| Regular octahedron of side s and mass m | 
|
[3] [3] |
|
| Regular dodecahedron of side s and mass m |
(where ) [3] |
||
| Regular icosahedron of side s and mass m | |||
| Hollow sphere of radius r and mass m. | 
|
[1] | |
| Solid sphere (ball) of radius r and mass m. | 
|
[1] | |
| Sphere (shell) of radius r2 and mass m, with centered spherical cavity of radius r1. | 
|
[1] | When the cavity radius r1 = 0, the object is a solid ball (above).
When r1 = r2, , and the object is a hollow sphere. |
| Right circular cone with radius r, height h and mass m | 
|
[4] About an axis passing through the tip: |
|
| Right circular hollow cone with radius r, height h and mass m | 
|
[4] [4] |
|
| Torus with minor radius a, major radius b and mass m. | 
|
About an axis passing through the center and perpendicular to the diameter: [5] About a diameter: [5] |
|
| Ellipsoid (solid) of semiaxes a, b, and c with mass m | 
|
[6] |
|
| Thin rectangular plate of height h, width w and mass m (Axis of rotation at the end of the plate) |

|
||
| Thin rectangular plate of height h, width w and mass m (Axis of rotation at the center) |

|
[1] | |
| Thin rectangular plate of mass m, length of side adjacent to side containing axis of rotation is r[a](Axis of rotation along a side of the plate) | |||
| Solid rectangular cuboid of height h, width w, and depth d, and mass m.[7] | 
|
For a similarly oriented cube with sides of length , | |
| Solid cuboid of height D, width W, and length L, and mass m, rotating about the longest diagonal. | 
|
For a cube with sides , . | |
| Tilted solid cuboid of depth d, width w, and length l, and mass m, rotating about the vertical axis (axis y as seen in figure). | 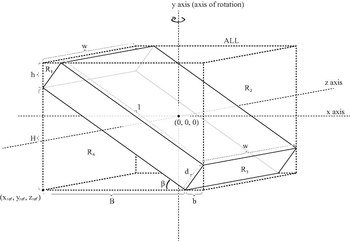
|
[8] | For a cube with sides , . |
| Triangle with vertices at the origin and at P and Q, with mass m, rotating about an axis perpendicular to the plane and passing through the origin. | |||
| Plane polygon with vertices P1, P2, P3, ..., PN and mass m uniformly distributed on its interior, rotating about an axis perpendicular to the plane and passing through the origin. | 
|
||
| Plane regular polygon with n-vertices and mass m uniformly distributed on its interior, rotating about an axis perpendicular to the plane and passing through its barycenter. R is the radius of the circumscribed circle. | [9] | ||
| An isosceles triangle of mass M, vertex angle 2β and common-side length L (axis through tip, perpendicular to plane) | 
|
[9] | |
| Infinite disk with mass distributed in a Bivariate Gaussian distribution on two axes around the axis of rotation with mass-density as a function of the position vector
|
|
List of 3D inertia tensors
[edit]This list of moment of inertia tensors is given for principal axes of each object.
To obtain the scalar moments of inertia I above, the tensor moment of inertia I is projected along some axis defined by a unit vector n according to the formula:
where the dots indicate tensor contraction and the Einstein summation convention is used. In the above table, n would be the unit Cartesian basis ex, ey, ez to obtain Ix, Iy, Iz respectively.
| Description | Figure | Moment of inertia tensor |
|---|---|---|
| Solid sphere of radius r and mass m | 
|
|
| Hollow sphere of radius r and mass m |  |
|
| Solid ellipsoid of semi-axes a, b, c and mass m | 
|
|
| Right circular cone with radius r, height h and mass m, about the apex | 
|
|
| Solid cuboid of width w, height h, depth d, and mass m |  |
|
| Slender rod along y-axis of length l and mass m about end |  |
|
| Slender rod along y-axis of length l and mass m about center |  |
|
| Solid cylinder of radius r, height h and mass m | 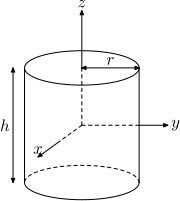 |
|
| Thick-walled cylindrical tube with open ends, of inner radius r1, outer radius r2, length h and mass m |  |
|
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Width perpendicular to the axis of rotation (side of plate); height (parallel to axis) is irrelevant.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i Raymond A. Serway (1986). Physics for Scientists and Engineers (2nd ed.). Saunders College Publishing. p. 202. ISBN 0-03-004534-7.
- ^ Classical Mechanics - Moment of inertia of a uniform hollow cylinder Archived 2008-02-07 at the Wayback Machine. LivePhysics.com. Retrieved on 2008-01-31.
- ^ a b c d e Satterly, John (1958). "The Moments of Inertia of Some Polyhedra". The Mathematical Gazette. 42 (339). Mathematical Association: 11–13. doi:10.2307/3608345. JSTOR 3608345. S2CID 125538455.
- ^ a b c d Ferdinand P. Beer and E. Russell Johnston, Jr (1984). Vector Mechanics for Engineers, fourth ed. McGraw-Hill. p. 911. ISBN 0-07-004389-2.
- ^ a b Eric W. Weisstein. "Moment of Inertia — Ring". Wolfram Research. Retrieved 2016-12-14.
- ^ Jeremy Tatum (14 April 2017). "2.20: Ellipses and Ellipsoids". phys.libretexts.org. Retrieved 1 May 2023.
- ^ see e.g. "Moment of Inertia J Calculation Formula". www.mikipulley.co.jp. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
- ^ A. Panagopoulos and G. Chalkiadakis. Moment of inertia of potentially tilted cuboids. Technical report, University of Southampton, 2015.
- ^ a b David Morin (2010). Introduction to Classical Mechanics: With Problems and Solutions; first edition (8 January 2010). Cambridge University Press. p. 320. ISBN 978-0521876223.











































































